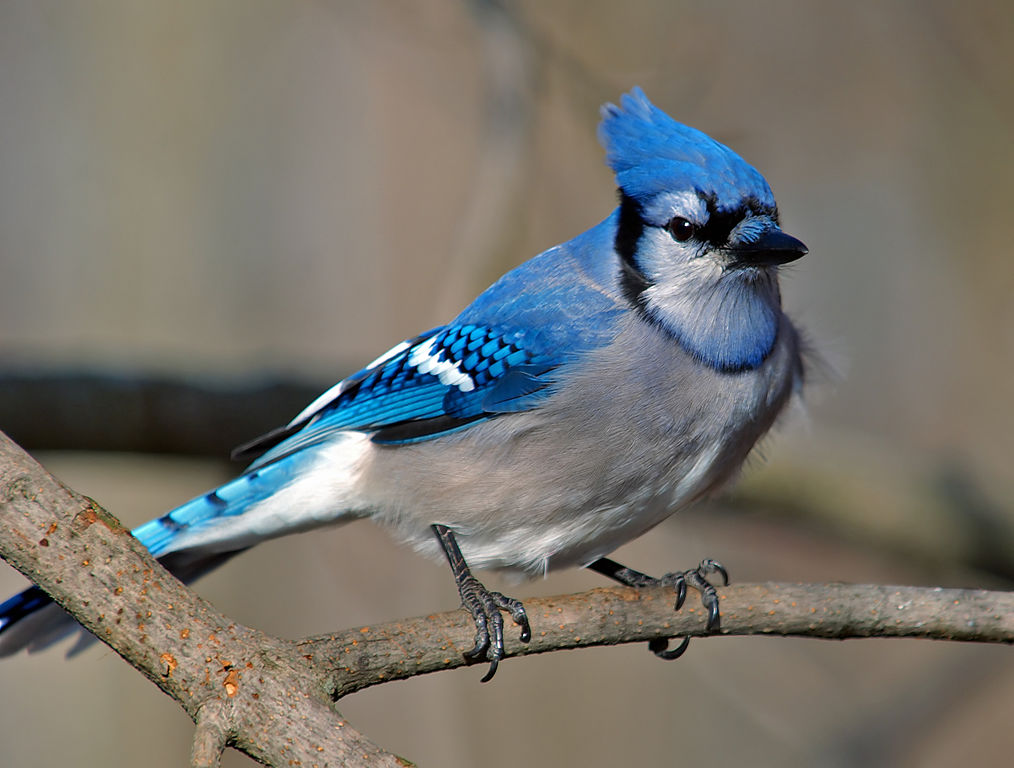
This common, expansive lark is recognizable to numerous individuals, with its peppy peak; blue, white, and dark plumage; and loud calls. Blue jays are known for their insights and complex social frameworks with tight family bonds. Their affection for oak seeds is credited with making a difference in spreading oak trees after the final frosty period.
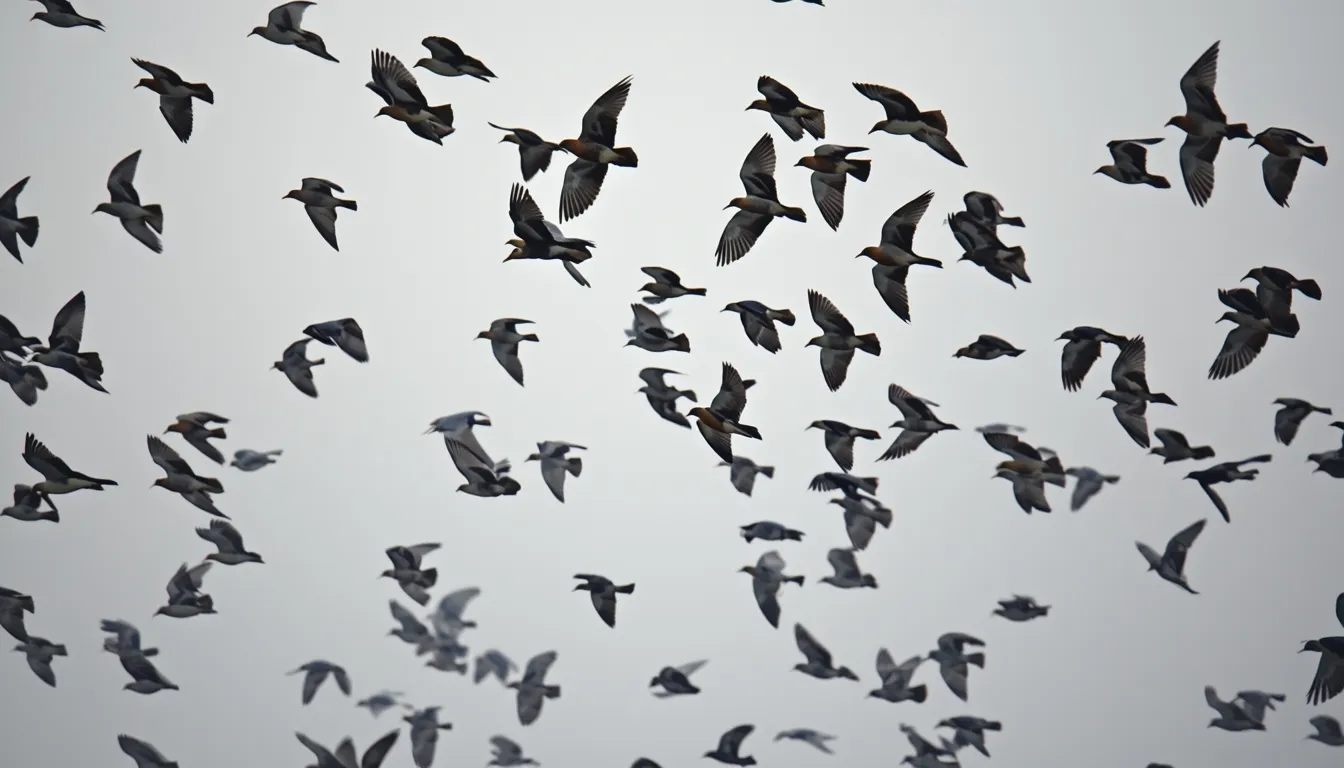
Blue jays are most frequently identified by their loud calls. Close to shorelines, they move in free herds; you can recognize them by their consistent flight, adjusted wings, long tail, and white underside. Inhabitant winged creatures may relate in herds; they ordinarily fly over open regions one at a time, frequently quietly. Moreover, observe them at feeders.
What Is the Meaning of the Blue Jay Cyanocitta Cristata?

Backyard Tips
Blue jays (Cyanocitta cristata) incline toward plate feeders or container feeders on a post or maybe hanging feeders, and they incline toward peanuts, sunflower seeds, and suet. Planting oak trees will make oak seeds accessible for jays of the future.
Read Also: Kakapo Bird Conservation: A Remarkable Comeback Story
Blue jays (Cyanocitta cristata) frequently take drinks from water basins. Discover more approximately what this winged creature likes to eat and what feeder is best by utilizing the Venture FeederWatch Common Feeder Feathered Creatures list.
Cool Facts
Thousands of blue jays (Cyanocitta cristata) move in herds along the Great Lakes and Atlantic coasts, but much around their movement remains a puzzle. A few are shown all through winter in all parts of their run.
Youthful jays may be more likely to move than grown-ups, but numerous grown-ups too move. A few person jays relocate south one year, remain north the next winter, and at that point move south once more the following year. No one has worked out why they relocate when they do.

Blue jays are known to take and eat eggs and nestlings of other winged creatures, but we don’t know how common this is. In a broad consideration of Blue Jay bolstering propensities, as it were, 1% of jays had proof of eggs or feathered creatures in their stomachs. Most of their slim-down was composed of creepy crawlies and nuts.
The blue jay habitually mimics the calls of birds of prey, particularly the red-shouldered sell. These calls may give data to other jays that a predator is around or may be utilized to misdirect other species into accepting a cell is present.
Tool utilization has never been detailed for wild blue jays, but captive blue jays utilized strips of daily paper to rake in nourishment pellets from outside their cages. Blue jays lower their peaks when they are nourishing calmly with family and run individuals or tending to nestlings.
At feeders in Florida, red-headed woodpeckers, Florida scrub-jays, common grackles, and gray squirrels unequivocally overwhelm blue jays, frequently preventing them from getting food. The color in blue jay plumes is melanin, which is brown.
The blue color is caused by diffusing light through altered cells on the surface of the plume barbs. The dark bridle over the crown, scruff, and throat shifts broadly and may offer assistance. Blue Jays recognize one another.
The most seasoned known wild, united Blue Jay was at least 26 years and 11 months old when it was found dead after being caught in angling equipment. It had been united in the Newfoundland/Labrador/St. Pierre et Miquelon range in 1989 and was found there in 2016.
The Four Keys to ID
Size & Shape: Expansive peaked lark with wide, adjusted tail. Blue jays are littler than crows and bigger than robins.
Color Design: White or light gray underneath, different shades of blue, dark, and white above.
What's the behavior of the blue jay, Cyanocitta cristata?
Blue jay Cyanocitta cristata makes an expansive assortment of calls that carry long distances. Most calls are created when the jay is roosted inside a tree. Ordinarily flies over open regions quietly, particularly amid relocation. Stuffs nourishment things in throat pocket to cache somewhere else; when eating, holds a seed or nut in feet and pecks it open.
Habitat: Blue Jays are feathered creatures of timberland edges. A favorite nourishment is oak seeds, and they are regularly found close to oaks in woodlands, woodlots, towns, cities, and parks.
What Does a Blue Jay (Cyanocitta Cristata) Eat?
Blue jays gather creepy crawlies and take nuts and seeds in trees, bushes, and on the ground; they moreover eat grains. They too take dead and harmed little vertebrates.
Blue Jays now and then attack homes for eggs and nestlings, and now and then pick up dead or passing-on grown-up fowls. Stomach substances over the years are almost 22 percent creepy crawly. Oak seeds, nuts, natural products, and grains made up nearly the whole leftover portion.
Of 530 stomachs inspected, traces of feathered creature eggs and nestlings were found in, as it were, 6 stomachs, in spite of the fact that an extraordinary look was made for each conceivable trace of feathered creature remains. Blue Jays hold nourishment things in their feet while pecking them open. They store nourishment in caches to eat later.
Nesting
Blue Jays construct their homes in the crotch or thick external branches of a deciduous or coniferous tree, as a rule 10-25 feet over the ground. Male and female both accumulate materials and construct the settle, but normally the male does more gathering and the female more building.
Twigs utilized in the external portion of the settle are, as a rule, taken from live trees, and fowls frequently battle to break them off. Winged creatures may fly extraordinary distances to get rootlets from recently burrowed trenches, new graves in cemeteries, and recently fallen trees. Jays may forsake their settlement after recognizing an adjacent predator.
Conservation
Blue Jays are common, but their populations have declined by an assessed 0.6% per year for an aggregate decrease of around 27% between 1966 and 2019, according to the North American Breeding Winged Creature Overview.
Accomplices in Flight gauges a worldwide breeding populace of 17 million. The species rates 9 out of 20 on the Mainland Concern Score, showing a species of moderate preservation concern. The most common cause of passing that is related to people comes from assaults by cats and mutts.
FAQ's- Blue Jay Cyanocitta Cristata
What is a Cyanocitta cristata?
The blue jay is between 9 and 12 inches in length. It is shinning blue on beat and white to gray on its throat, chest and stomach. It has a gray-blue peak on its head and dark and white bars on its wings and tail. Its charge, legs and feet are black.
What does the blue jay symbolize?
Cultural Noteworthiness and Imagery: Blue Jays hold different typical implications over societies. Their striking appearance has driven to affiliations with truth, communication, and dependability. In a few Local American convictions, Blue Jays speak to cleverness and adaptability.
What is the distinction between a cristata and a torch?
Cristata Burn Corals are exceptionally comparable to standard Long Limb Burn Corals (E. glabrescent) but have much shorter appendages and are distant less common. This WYSIWYG frag is a single huge head. Euphyllia have been a installation in reef aquariums apparently since the side interest began.
Is seeing a blue jay great or awful luck?
Despite there being no real say of them in the Book of scriptures, numerous ardent Christians in America accept that blue jays are signs from God and to see one close or at your property implies great things are coming.
Why are burn corals so expensive?
LPS coral such as Pound and Burn Coral were not as prevalent since there were as it were a few sorts and they were a bit more troublesome to keep lively. Presently, there are more varieties than ever some time recently, and its Exceptionally Simple to keep these coral. With that, presently these coral are more well known, making them more expensive.
What does a blue jay eat?
Blue Jays gather creepy crawlies and take nuts and seeds in trees, bushes, and on the ground; they too eat grains. They too take dead and harmed little vertebrates. Blue Jays some of the time strike homes for eggs and nestlings, and now and then choose up dead or passing on grown-up feathered creatures.